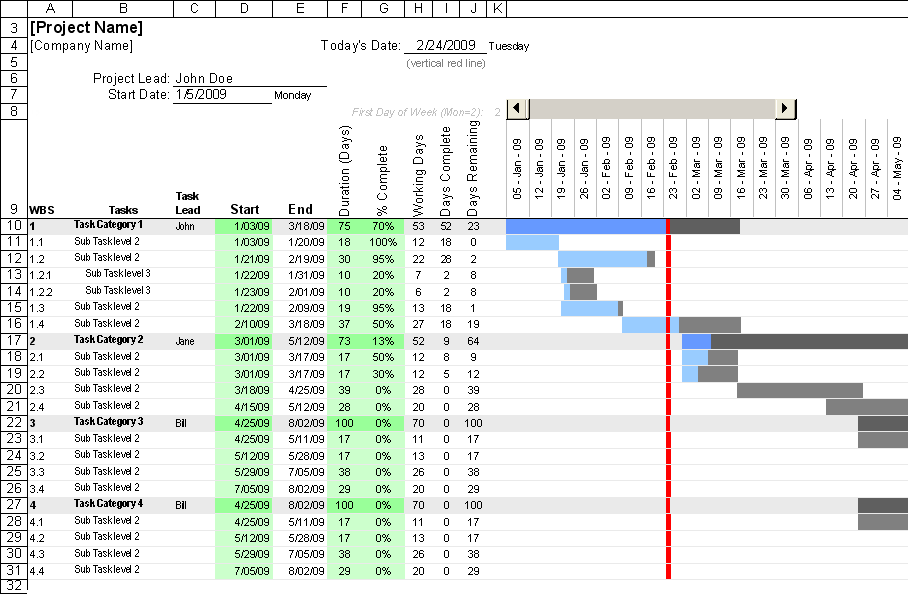
Week 11: Product Management
1) Explain the triple constraint and its importance in project management.
The triple constraint involves making trade-offs between scope, time and cost for a project. It is inevitable in a project life cycle that there will be changes to the scope, time or cost of the project.
2) Describe two primary diagrams most frequently used in project planning.
GANTT Charts - a simple bar chart that depicts project tasks against a calendar
PERT Chart - a graphical network model that depicts a project’s tasks and the relationships between those tasks
3) Identify three primary areas a project manager must focus on managing to ensure success.
- Managing People
- Managing Communications
- Managing Change
4) Outline the two reasons why projects fail and two reasons why they succeed.
Why they fail:
- Unrealistic expectations; whilst aiming high is a good thing, businesses who aim too high without the correct resources (money, staff, time) will have their projects fail.
- Politics; internal factor where not everyone agrees successfully get along
Why they succeed:
- Team Members are working towards a common goal
- Good communication
Business IT Blog
Tuesday, 1 November 2011
Week 10: Customer Relationship Management and Business Intelligence
1) What is your understanding of CRM?
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is a widely implemented strategy for managing company's interactions with customers, clients and sales prospects. It involves using technology to organize, automate and synchronise business processes.
7) What are two possible outcomes a company could get from using data mining?
Data mining is the application of statistical techniques to find patterns and relationships among data and to classify and predict. Two possible outcomes are
- Cluster Analysis
- Statistical Analysis
Cluster analysis is a technique used to divide information into mutually exclusive groups. CRM systems depend on cluster analysis to segment customer information and identify behavioural traits.
Statistical Analysis on the other hand performs functions as information correlations distributions, calculations and variance analysis
1) What is your understanding of CRM?
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is a widely implemented strategy for managing company's interactions with customers, clients and sales prospects. It involves using technology to organize, automate and synchronise business processes.
2) Compare operational and analytical customer relationship management.
Operational Customer Relationship Management supports transactional processing for day-to-day front office operations or systems that deal directly with the customer whereas Analytical CRM supports back-office operations and strategic analysis. It includes all systems that do not deal directly with the customers.
3) Describe and differentiate the CRM technologies used by marketing departments and sales departments.
Operational CRM focuses on organising and simplifying the management of customer information. It uses a database to provide consistent information about a company's interaction with the customer.
CRM metrics are another tool used by businesses. It is used to track and monitor performance and is the best practice for many companies.
Sales Metrics:
- Number of prospective customers
- Number of new customers
- Number of retained customers
Marketing Metrics:
- Number of marketing campaigns
- New customer retention rates
- Number of responses by marketing campaigns
4) How could a sales departments use operational CRM technologies?
There are three marketing operational CRM technologies that are used by businesses. These include:
1. List generator: compiles customer information from a variety of sources and segment the information for different marketing campaigns
2 Campaign Management System: guides users through marketing campaigns
3. Cross-selling and up-selling: cross selling is the selling of additional products of services while up-selling increases the value of the sale.
5) Describe business intelligence and its value to businesses
Business intelligence uses applications and technologies used to gather, provide access to, and analyze data and information to support decision-making efforts. Business Intelligence includes simple MS Excel Pivot tables to highly sophisticated software that fetches data from the different front and back-office systems.
6) Explain the problem associated with business intelligence. Describe the solution to fix this business problem.
The main problem that is associated with businesses today is data rich, information poor. Businesses are
finding it close to impossible to understand their own strengths and weaknesses let alone those of their competitors. The reason for this is that businesses have too much information and a lot of it is not accessible by anyone besides the IT department.7) What are two possible outcomes a company could get from using data mining?
Data mining is the application of statistical techniques to find patterns and relationships among data and to classify and predict. Two possible outcomes are
- Cluster Analysis
- Statistical Analysis
Cluster analysis is a technique used to divide information into mutually exclusive groups. CRM systems depend on cluster analysis to segment customer information and identify behavioural traits.
Statistical Analysis on the other hand performs functions as information correlations distributions, calculations and variance analysis
Monday, 31 October 2011
Week 9: Operations Management and Supply Chain
6) Define the relationship between information technology and the supply chain.
All data is related to demand, shipments, orders, returns and schedules as well as changes in any of these data. I.T's primary role is to create integrations or tight process and information linkages between functions within an organisation. Integrated Systems provide companies with greater visibility over the supply chain inventory levels. Technology advances and significantly improves companies' forecasting and business operations.
1) Define the term operations management
Operations management is the management of systems or processes that converts or transforms resources into goods and services.
Operations management is the management of systems or processes that converts or transforms resources into goods and services.
2) Explain operations management’s role in business
answers.com states that the roles of operations management is to co-ordinate the activities of all the factors of production namely; labour, land, capital, technology and equipments.
3) Describe the correlation between operations management and information technology
Managers use IT to heavily influence OM decisions, including
- What: What resources will be needed and in what amounts?
- When: when should work be scheduled?- Where: where will the work be performed?- How: How will the work be done?
- Who: who will perform the work?
4) Explain supply chain management and its role in a business
Supply chain; a network of organisations and facilities that transforms raw materials into the products that are delivered to customers.
answers.com states that the roles of operations management is to co-ordinate the activities of all the factors of production namely; labour, land, capital, technology and equipments.
Managers use IT to heavily influence OM decisions, including
- What: What resources will be needed and in what amounts?
- When: when should work be scheduled?- Where: where will the work be performed?- How: How will the work be done?
- Who: who will perform the work?
4) Explain supply chain management and its role in a business
Supply chain; a network of organisations and facilities that transforms raw materials into the products that are delivered to customers.
This video may be helpful to understand Supply Chain Management.
5) List and describe the five components of a typical supply chain
6) Define the relationship between information technology and the supply chain.
All data is related to demand, shipments, orders, returns and schedules as well as changes in any of these data. I.T's primary role is to create integrations or tight process and information linkages between functions within an organisation. Integrated Systems provide companies with greater visibility over the supply chain inventory levels. Technology advances and significantly improves companies' forecasting and business operations.
Monday, 10 October 2011
Week 8: Databases and Data Warehouses
A data warehouse is the logical collection of information, gathered from many different operational databases, that supports business analysis activities and decision-making tasks. The primary purpose of a data warehouse is to aggregate information throughout an organisation into a single repository for decision-making purposes.
1) List, describe and provide an example of each of the five characteristics of high quality information
- Accuracy: are all values correct? For example, is the name spelt correctly? is the dollar amount recorded properly?
- Completeness: are any of the values missing? For example, is the address complete including street, city, state and postcode?
- Consistency: Is aggregate or summary information in agreement with detailed information? For example, do all total fields equal the true total of the individual fields?
- Uniqueness: Is each transaction, entity and event represented only once in the information? For example, do all the total fields equal the true total of the individual fields?
- Timeliness: Is the information current with respect to the business requirements? For example, is information updated weekly, daily, or hourly?
2) Define the relationship between a database and a database management system.
A database in an organised collection of data. A database management system is a group of programs that manipulate the database. It provides an interface between the database and its users and other application programs.
3) Describe the advantages an organisation can gain by using a database.
A Database is the heart of an organisation, it stores key business information such as:
- Sales data; customers, sales, contacts
- Inventory data; orders, stock, delivery
- Student data; names, address, grades
4) Describe the fundamental concepts of the relational database model.
A relational database is a type of database that stores information in the form of logically related two-dimensional tables each consisting of rows and columns. This allows data to be accessed in many different ways without having to reorganise the database tables.
5) Describe the benefits of a data-driven website
Data-driven websites are an interactive website kept constantly updated and relevant to the needs of its customers through the use of a database. These advantages include:
- Development
- Content management
- Future expandability
- Minimising human error
- Cutting production and update costs
- More efficient
- Improved stability
- Real time info like stock levels and price changes
6) Describe the roles and purposes of data warehouses and data marts in an organisation.
A data warehouse is the logical collection of information, gathered from many different operational databases, that supports business analysis activities and decision-making tasks. The primary purpose of a data warehouse is to aggregate information throughout an organisation into a single repository for decision-making purposes.
Friday, 16 September 2011
Week 7: Networks and Wireless
1) Explain the business benefits of using wireless technology.
Wireless technology is a beneficial aspect for businesses. It allows access to more information and files such as customer or employee information. It extends to places that cable and fiber are unable to and provides broadband access extension. It reduces costs and can be assembled and brought online in 2-3 hours.
2) Describe the business benefits associated with VOIP
VOIP stands for voice over internet protocol. It enables phone calls, faxes, voice mail, email and web conferences over digital networks.
It can be beneficial for businesses as it reduces communication and infrastructure costs. It facilitates tasks and provides services that may be harder to implement using the Public switched telephone network (PSTN).
3) Compare LANs and WANs
Local area networks (LAN) connect computers that are located in a single geographic location on the premises of a company that operates LANs. However, wide are networks (WAN) connect computers from differing geographic sites.
4) Describe RFID and how it can be used to help make a supply chain more effective.
Radio frequency identification (RFID) tags use radio waves for the transmission of data. Shipments can be identified with RFID smart labels that enable unattended ID, verification and the sorting of data at different points in the supply chain across trading partners and distribution centers.
zebra.com can assist with any additional required information.
5) What is one new emerging technology that could change a specific industry?
An emerging technology that could change a specific industry includes ‘Pay Buy Mobile’’ impacting the mobile phone industry. It would merge financial and mobile industries together.
gsmworld.com can assist with any additional required information.
Week 6: Enterprise Architectures
1) What is information architecture and what is information infrastructure and how do they differ and how do they relate to each other?
Information architecture is a general plan of how IT is to be used within an organisation, that is, useful for planning. It identifies where and how important information is maintained and secured. It should also focus on backup and recovery, disaster recovery and information security.
IT infrastructure is the actual implementation stage that will provide for effective information systems, including hardware, software, services as well as the people involved. It includes equipment for all hardware, software and telecommunications activities that provide the underlying foundation to support the organisation's goals when combined.
2) Describe how an organisation can implement a solid information architecture
An organisation can implement solid information architecture by having a strong information security plan, managing user access and having up-to-date antivirus software and patches.
3) List and describe the five requirement characteristics of infrastructure architecture.
The five required characteristics of infrastructure and architecture include:
1.Reliability:
- high accuracy
- low accuracy puts the organisation at risk
2. Scalability
- systems ability to meet growth requirements
capacity planning
3. Flexibility
- ability to meet changing business demands
- may involve multinational challenges
4. Availability
- high availability 99.99% uptime
- ensures business continuity
5. Performance
- how quickly a system performs a certain task
- growing pressure on systems to be faster
4) Describe the business value in deploying a service oriented architecture.
An event is an electronic message that indicates something has happened. It detects threats and opportunities and alerts those who can act on the information
6) What is a service?
A service contains a set of related commands that can be re-used. It is more like a software product as opposed to a coding product.
7) What emerging technologies can companies use to increase performance and utilise their infrastructure more effectively?
The emerging technologies that companies can use to increase performance and utilise their infrastructure more effectively include:
- Service
- Interoperability
- Loose coupling
- Virtualisation
1) What is information architecture and what is information infrastructure and how do they differ and how do they relate to each other?
Information architecture is a general plan of how IT is to be used within an organisation, that is, useful for planning. It identifies where and how important information is maintained and secured. It should also focus on backup and recovery, disaster recovery and information security.
IT infrastructure is the actual implementation stage that will provide for effective information systems, including hardware, software, services as well as the people involved. It includes equipment for all hardware, software and telecommunications activities that provide the underlying foundation to support the organisation's goals when combined.
2) Describe how an organisation can implement a solid information architecture
An organisation can implement solid information architecture by having a strong information security plan, managing user access and having up-to-date antivirus software and patches.
3) List and describe the five requirement characteristics of infrastructure architecture.
The five required characteristics of infrastructure and architecture include:
1.Reliability:
- high accuracy
- low accuracy puts the organisation at risk
2. Scalability
- systems ability to meet growth requirements
capacity planning
3. Flexibility
- ability to meet changing business demands
- may involve multinational challenges
4. Availability
- high availability 99.99% uptime
- ensures business continuity
5. Performance
- how quickly a system performs a certain task
- growing pressure on systems to be faster
4) Describe the business value in deploying a service oriented architecture.
Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) is a business-driven IT architectural approach that supports integrating a business as linked, repeatable tasks or services. It ensures IT systems can adapt quickly, easily and economically to support rapidly changing business needs. A SOA allows enterprises to plug in new services or upgrade existing services in a granular fashion. As well it responds more quickly and is cost-effective to changes in market-conditions.
5) What is an event?An event is an electronic message that indicates something has happened. It detects threats and opportunities and alerts those who can act on the information
6) What is a service?
A service contains a set of related commands that can be re-used. It is more like a software product as opposed to a coding product.
7) What emerging technologies can companies use to increase performance and utilise their infrastructure more effectively?
The emerging technologies that companies can use to increase performance and utilise their infrastructure more effectively include:
- Service
- Interoperability
- Loose coupling
- Virtualisation
Week 5: Ethics and Security
1) Explain the ethical issues surrounding information technology
One ethical issue surrounding IT is intellectual property, which is the collection of rights that protect creative and intelllectual effort. Copyright is another issue, surrounding the exclusive right to do, or omit to do, certain acts with intangible property such as a song, video game and some types of proprietary documents. Fair use of doctrine is also an ethical issue, dealing with how in certain situations, it is legal to use copyrighted material. Pirated software is the unauthorised use, duplication distribution, or sale of copyrighted software, hence why it is an ethical issue. Counterfeit software is also an example of ethical issues surrounding IT, being software that is manufactured to look like the real thing and sold as such.
2) Describe a situation involving technology that is ethical but illegal
A situation involving technology that is ethical but illegal includes making an extra copy of a software package that you purchased and keeping one on file for backup.
3) Describe and explain one of the computer use policies that a company might employ
An ethical computer use policy contains general principles to guide computer use behaviour. For example, the ethical computer use policy might explicitly state that users should refrain from playing computer games during working hours. this policy ensures the users know how to behave at work and the organisation has a published standard by which to deal with user infractions.
4) What are the 5 main technology security risks?
The five main technology security risks are:
- Human error
- Natural disasters
- Technical failures
- Deliberate acts
- Management failure
5) Outline one way to reduce each risk
One way to reduce human error risks and malicious acts can be reduced with the use of a strong password incorporating letters and numbers, and regularly changed to ensure a high level of security. This makes it more difficult for hackers and other unauthorised users to frequently access your information.
There is no way to prevent Natural disasters however a company can prepare themselves efficiently in case of this event and have all files backed up and alternative plans.
Technical failures are most of the time unforeseen and cannot be predicted therefore organisations must ensure they have all files backed up and frequently saved so that if systems were to crash, their data and unsaved files will not be lost.
6) What is a disaster recovery plan, what strategies might a firm employ?
A disaster recovery plan is the process of regaining access to a computer systems and its data after a disaster has occurred. It is encouraged that all firms have a comprehensive disaster recovery plan set. This plan lists things such as communication plans, alternative sites, business continuity and location of backup data. All firms must have business continuity plans which outlines in detail what happens in the case of a disaster, offsite data kept in date order, hot or warm sites, well documented procedures and regular recovery testing.
1) Explain the ethical issues surrounding information technology
One ethical issue surrounding IT is intellectual property, which is the collection of rights that protect creative and intelllectual effort. Copyright is another issue, surrounding the exclusive right to do, or omit to do, certain acts with intangible property such as a song, video game and some types of proprietary documents. Fair use of doctrine is also an ethical issue, dealing with how in certain situations, it is legal to use copyrighted material. Pirated software is the unauthorised use, duplication distribution, or sale of copyrighted software, hence why it is an ethical issue. Counterfeit software is also an example of ethical issues surrounding IT, being software that is manufactured to look like the real thing and sold as such.
2) Describe a situation involving technology that is ethical but illegal
A situation involving technology that is ethical but illegal includes making an extra copy of a software package that you purchased and keeping one on file for backup.
3) Describe and explain one of the computer use policies that a company might employ
An ethical computer use policy contains general principles to guide computer use behaviour. For example, the ethical computer use policy might explicitly state that users should refrain from playing computer games during working hours. this policy ensures the users know how to behave at work and the organisation has a published standard by which to deal with user infractions.
4) What are the 5 main technology security risks?
The five main technology security risks are:
- Human error
- Natural disasters
- Technical failures
- Deliberate acts
- Management failure
5) Outline one way to reduce each risk
One way to reduce human error risks and malicious acts can be reduced with the use of a strong password incorporating letters and numbers, and regularly changed to ensure a high level of security. This makes it more difficult for hackers and other unauthorised users to frequently access your information.
There is no way to prevent Natural disasters however a company can prepare themselves efficiently in case of this event and have all files backed up and alternative plans.
Technical failures are most of the time unforeseen and cannot be predicted therefore organisations must ensure they have all files backed up and frequently saved so that if systems were to crash, their data and unsaved files will not be lost.
6) What is a disaster recovery plan, what strategies might a firm employ?
A disaster recovery plan is the process of regaining access to a computer systems and its data after a disaster has occurred. It is encouraged that all firms have a comprehensive disaster recovery plan set. This plan lists things such as communication plans, alternative sites, business continuity and location of backup data. All firms must have business continuity plans which outlines in detail what happens in the case of a disaster, offsite data kept in date order, hot or warm sites, well documented procedures and regular recovery testing.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)